Running tasks
Running tasks on computers
From the Network page, you can remotely run a number of administrative tasks on computers.
This is the list of tasks you can run:
You can choose to create tasks individually for each computer or for groups of computers. For example, you can remotely install the security agent on a group of unmanaged computers. At a later time, you can create a scan task for a certain computer from the same group.
For each computer, you can only run compatible tasks. For example, if you select an unmanaged computer, you can only choose to install the security agent, all the other tasks being disabled.
For a group, the selected task will be created only for compatible computers. If none of the computers in the group is compatible with the selected task, you will be notified that the task could not be created.
Once created, the task will start running immediately on the online computers. If a computer is offline, the task will run as soon as it gets back online.
You can view and manage the task in the Network > Tasks page. For more information, refer to Viewing and managing tasks.
Malware scan
To remotely run a scan task on one or several computers:
Go to the Network page.
Choose Computers and Virtual Machines from the views selector.
Select the container that you want from the left-side pane. All computers from the selected container are displayed in the right-side pane table.
Select the check boxes of computers or groups you want to scan.
Click the
 Tasks button at the upper side of the table and choose Malware scan.
Tasks button at the upper side of the table and choose Malware scan.A configuration window will appear.
Configure the scan options:
In the General tab, you can choose the type of scan and you can enter a name for the scan task.
The scan task name is intended to help you easily identify the current scan in the Tasks page.
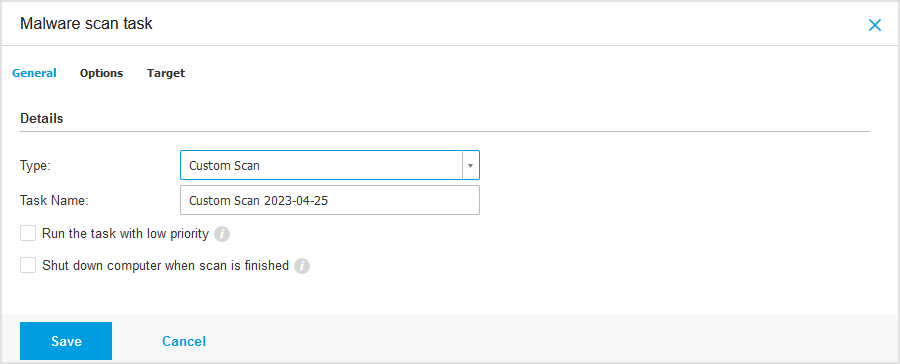
Select the type of scan from the Type menu:
Quick scan uses in-the-cloud scanning to detect malware running in the system. This type of scan is preconfigured to allow scanning only critical Windows and Linux system locations. Running a Quick Scan usually takes less than a minute and uses a fraction of the system resources needed by a regular virus scan.
When malware or rootkits are found, Bitdefender automatically proceeds with disinfection. If, for any reason, the file cannot be disinfected, then it is moved to quarantine. This type of scanning ignores suspicious files.
Full scan checks the entire system for all types of malware threatening its security, such as viruses, spyware, adware, rootkits and others.
Bitdefender automatically tries to disinfect files detected with malware. In case malware cannot be removed, it is contained in quarantine, where it cannot do any harm. Suspicious files are being ignored. If you want to take action on suspicious files as well, or if you want other default actions for infected files, then choose to run a Custom Scan.
Memory scan checks the programs running in the computer's memory.
Network scan is a type of custom scan, allowing to scan network drives using the Bitdefender security agent installed on the target endpoint.
For the network scan task to work:
You need to assign the task to one single endpoint in your network.
You need to enter the credentials of a user account with read/write permissions on the target network drives, for the security agent to be able to access and take actions on these network drives. The required credentials can be configured in the Target tab of the tasks window.
Custom scan allows you to choose the locations to be scanned and to configure the scan options.
For memory, network and custom scans, you have also these options:
Run the task with low priority. Select this check box to decrease the priority of the scan process and allow other programs to run faster. This will increase the time needed for the scan process to finish.
On ARM-based macOS endpoints, the security agent optimizes the scan process depending on the processor usage. At over 50% usage, the scan process relocates to the efficiency cores, while at over 80% the task pauses until the processor usage drops below this threshold.
Shut down computer when scan is finished. Select this check box to turn off your machine if you do not intend to use it for a while.
For custom scans, configure the following settings:
Go to the Options tab to set the scan options.
Click the security level that best suits your needs (Aggressive, Normal or Permissive).
Use the description on the right-side of the scale to guide your choice.
Based on the selected profile, the scan options in the Settings section are automatically configured. However, if you want to, you can configure them in detail. To do that, select the Custom check box and then expand the Settings section.

The following options are available:
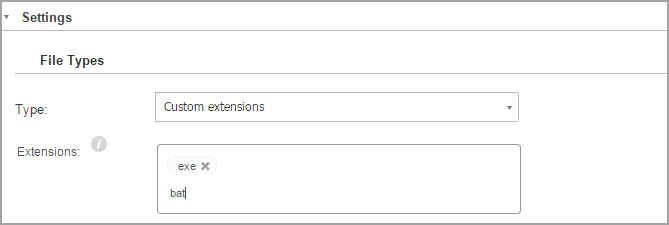
File types
Use these options to specify which types of files you want to be scanned.
You can set the security agent to scan all files (regardless of their file extension), application files only or specific file extensions you consider to be dangerous.
Scanning all files provides best protection, while scanning applications only can be used to perform a quicker scan.
Note
Application files are far more vulnerable to malware attacks than other types of files.
For more information, refer to Application file types.
If you want only specific extensions to be scanned, choose Custom extensions from the menu and then enter the extensions in the edit field, pressing
Enterafter each extension.Important
Bitdefender security agents installed on Windows and Linux operating systems scan most of the .ISO formats, but does not take any action on them.
Archives
Archives containing infected files are not an immediate threat to system security.
The malware can affect the system only if the infected file is extracted from the archive and executed without having real-time protection enabled.
However, it is recommended to scan archives in order to detect and remove any potential threat, even if it is not an immediate threat.
Important
Scanning archived files increases the overall scanning time and requires more system resources.
Scan inside archives
Select this option if you want to check archived files for malware.
If you decide on using this option, you can configure the following optimization options:
Limit archive size to (MB)
You can set a maximum accepted size limit of archives to be scanned.
Select the corresponding check box and type the maximum archive size (in MB).
Maximum archive depth (levels)
Select the corresponding check box and choose the maximum archive depth from the menu.
For best performance choose the lowest value, for maximum protection choose the highest value.
Scan email archives
Select this option if you want to enable scanning of email message files and email databases, including file formats such as .eml, .msg, .pst, .dbx, .mbx, .tbb and others.
Important
Email archive scanning is resource intensive and can impact system performance.
Miscellaneous
Select the corresponding check boxes to enable the desired scan options.
Scan boot sectors
Scans the system’s boot sector.
This sector of the hard disk contains the necessary computer code to start the boot process.
When a virus infects the boot sector, the drive may become inaccessible and you may not be able to start your system and access your data.
Scan registry
Select this option to scan registry keys.
Windows Registry is a database that stores configuration settings and options for the Windows operating system components, as well as for installed applications.
Scan for rootkits
Select this option to scan for glossary.rootkit rootkits and objects hidden using such software.
Scan for keyloggers
Select this option to scan for glossary.keylogger keylogger software.
Scan network shares
This option scans mounted network drives.
For quick scans, this option is deactivated by default. For full scans, it is activated by default. For custom scans, if you set the security level to Aggressive/Normal, the Scan network shares option is automatically enabled. If you set the security level to Permissive, the Scan network shares option is automatically disabled.
Scan memory
Select this option to scan programs running in the system's memory.
Scan cookies
Select this option to scan the cookies stored by browsers on the computer.
Scan only new and changed files
By scanning only new and changed files, you may greatly improve overall system responsiveness with a minimum trade-off in security.
Scan for Potentially Unwanted Applications (PUA)
A Potentially Unwanted Application (PUA) is a program that may be unwanted on the PC and sometimes comes bundled with freeware software. Such programs can be installed without the user's consent (also called adware) or will be included by default in the express installation kit (ad-supported). Potential effects of these programs include the display of pop-ups, installing unwanted toolbars in the default browser or running several processes in the background and slowing down the PC performance.
Preserve last access time
This option helps you control whether to preserve the last access time for a file during a scan or to allow the scanning process to modify the timestamp of that file. The option is enabled by default.
Scan detachable volumes
Select this option to scan any removable storage drive attached to the computer.
Actions
Depending on the type of detected file, the following actions are taken automatically:
When an infected file is found
Bitdefender detects files as infected through various advanced mechanisms, which include malware signatures, machine learning and artificial intelligence (AI) based technologies.
The Bitdefender security agent can normally remove the malware code from an infected file and reconstruct the original file. This operation is known as disinfection.
By default, if an infected file is detected, the Bitdefender security agent will automatically attempt to disinfect it.
If disinfection fails, the file is moved to quarantine in order to contain the infection.
Important
For particular types of malware, disinfection is not possible because the detected file is entirely malicious. In such cases, the infected file is deleted from the disk.
When a suspect file is found
Files are detected as suspicious by the heuristic analysis and other Bitdefender technologies.
These provide a high detection rate, but the users must be aware of certain false positives (clean files detected as suspicious) in some cases.
Suspect files cannot be disinfected, because no disinfection routine is available.
Scan tasks are configured by default to ignore suspect files.
You may want to change the default action in order to move suspect files to quarantine.
Quarantined files are sent for analysis to Bitdefender Labs on a regular basis.
If malware presence is confirmed, a signature is released to allow removing the malware.
When a rootkit is found
Rootkits represent specialized software used to hide files from the operating system.
Though not malicious in nature, rootkits are often used to hide malware or to conceal the presence of an intruder into the system.
Detected rootkits and hidden files are ignored by default.
Though not recommended, you can change the default actions.
You can specify a second action to be taken if the first one fails and different actions for each category.
Choose from the corresponding menus the first and the second action to be taken on each type of detected file.
The following actions are available:
Disinfect
Remove the malware code from infected files.
It is recommended to always keep this as the first action to be taken on infected files.
Move files to quarantine
Move detected files from their current location to the quarantine folder.
Quarantined files cannot be executed or opened; therefore, the risk of getting infected disappears.
You can manage quarantine files from the quarantine Quarantine page of the console.
Delete
Delete detected files from the disk, without any warning.
It is advisable to avoid using this action.
Ignore
No action will be taken on detected files. These files will only appear in the scan log.
Go to Target tab to configure the locations you want to be scanned on the target computers.
In the Scan target section you can add a new file or folder to be scanned:
Choose a predefined location from the drop-down menu or enter the Specific paths you want to scan.
Specify the path to the object to be scanned in the edit field.
If you have chosen a predefined location, complete the path as needed.
For example, to scan the entire
Program Filesfolder, it suffices to select the corresponding predefined location from the drop-down menu.To scan a specific folder from
Program Files, you must complete the path by adding a backslash (\) and the folder name.If you have chosen Specific paths, enter the full path to the object to be scanned.
It is advisable to use system variables (where appropriate) to make sure the path is valid on all target computers. For more information regarding system variables, refer to appendices.variables.
Click the corresponding add_inline.png Add button.
To edit an existing location, click it.
To remove a location from the list, click the corresponding elete_inline.png Delete button.
For network scan tasks, you need to enter the credentials of a user account with read/write permissions on the target network drives, for the security agent to be able to access and take actions on these network drives.
Click the Exclusions section if you want to define target exclusions.
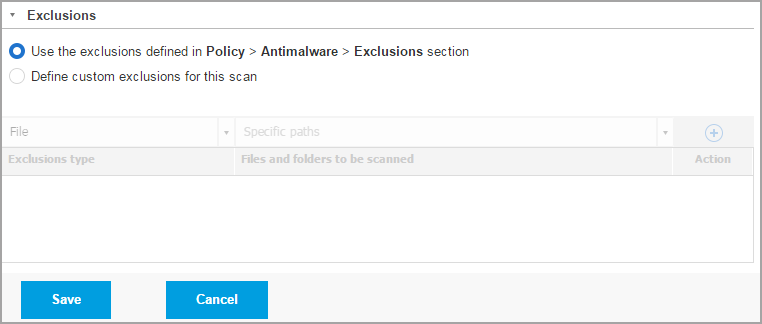
You can either use the exclusions defined by policy or define explicit exclusions for the current scan task.
For more details regarding exclusions, refer to Settings.
Click Save to create the scan task. A confirmation message will appear.
You can view and manage the task on the Network > Tasks page. For more information, refer to Viewing and managing tasks.
Note
To schedule a scan task, go to the Policies page, select the policy assigned to the computers you are interested in, and add a scan task in the Antimalware > On-demand section. For more information, refer to On-demand.
IOC scan
At any time, you can choose to run on-demand scanning for known Indicators of Compromise (IOC) on selected endpoints.
Important
This task is only available for plans that include the EDR / XDR feature.
Running an IOC scan task
To run an IOC scan task, follow these steps:
Go to the Network page.
Browse the containers and select the endpoints you want to scan.
Click the
 Tasks button and choose IOC scan.
Tasks button and choose IOC scan.A configuration page will appear, where you need to select the type of indicators taken into account for IOC scanning.
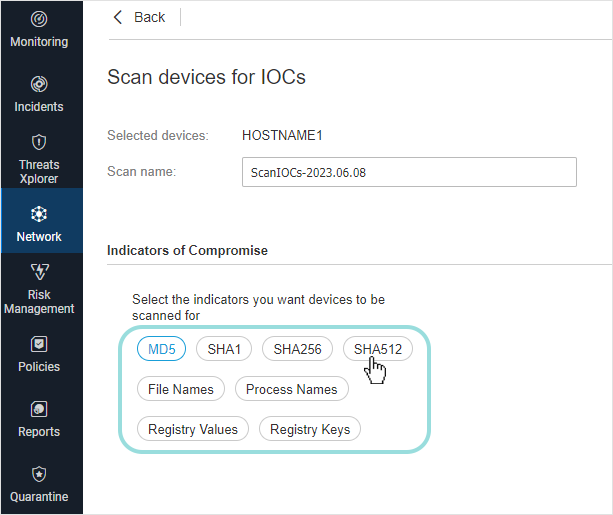
Important
You must select at least one type of Indicator of Compromise to create a valid task.
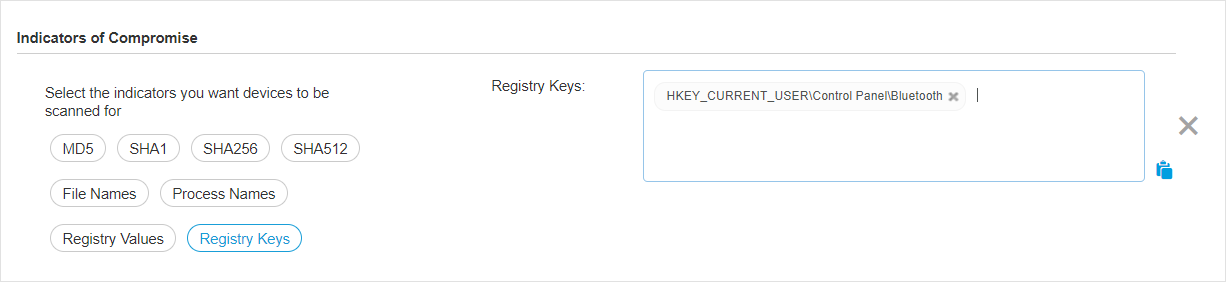
Select one or more IOC types you want to take into account for scanning and write the known IOC name in the newly added field.
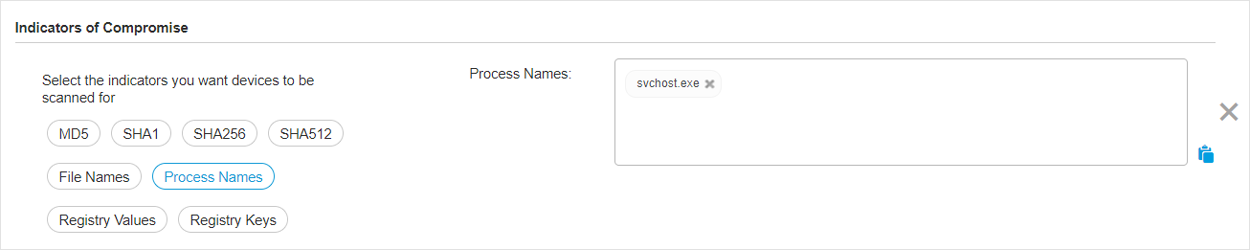
You can select from the following types:
MD5
SHA1
SHA256
SHA512
File Names
Process Names
Registry Values
Registry Keys
Note
Content added inside each field must be valid. Otherwise, you will be prompted with a warning sign and a message.
Click Save to create and run the IOC scan task.
A confirmation message will appear.
You can check the task's progress in the Network > Tasks page.
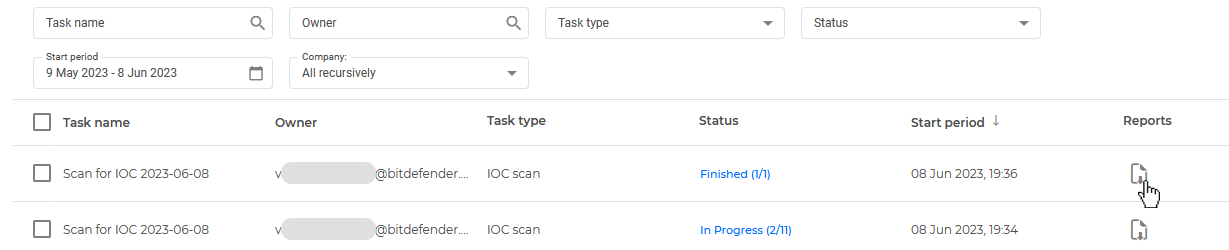
Once the task has finished successfully, you can click the
 Reports button to read the report generated and assess the impact of the IOC you scanned for.
Reports button to read the report generated and assess the impact of the IOC you scanned for.
Formatting for IOC scan fields
The File Names and Process Names fields accept as input any of the following:
file names or process names, for example,
malware.exeabsolute file paths, for example,
C:\Users\User1\Downloads\malware.exefile paths that contain:
variables, for example,
%AppData%\Malware\malware.exeThese variables refer to Windows Known Folders. Only use these variables at the beginning of the file path.
wildcard characters, for example,
**\AppData\**\*.exeThere are three types of supported wildcard characters:
?- matches any one character*- matches zero or more characters, excluding the\and/characters.**- matches zero or more characters, including the\and/characters.
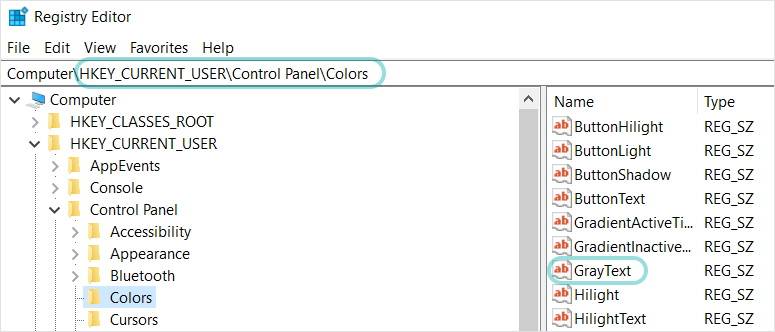
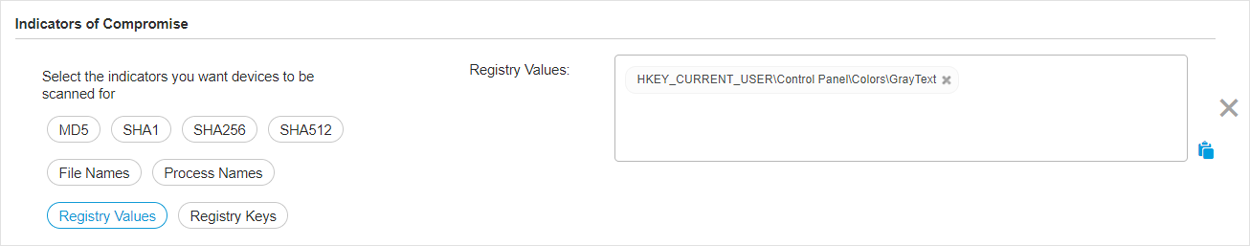
Use the Registry Values field to scan for registry value names. Your input must contain the full path to the registry value. See the example below.
Use the Registry Keys field to scan for registry keys and subkeys. Your input must contain the full path to the registry key or subkey. See the example below.
IOC scan limitations
Valid file extensions for IOCs added to the task include: exe, dll, com, scr, jar, msi, msc, bat, ps1, vbs, vbe, js, jse, wsf, wsh, psc1, lnk, doc, docx, docm, xls, xlsx, xlsm, ppt, pptx, pptm, eml, rtf, pdf, html, ppsx, pps, ppsm, pot, potx, potm, ocx, sys, fnr, fne, and pif.
The Scan for IOC task will scan the following locations:
%Windows%\System32\Drivers%Windows%\System32\WindowsPowerShell\v1.0%Windows%\system32\config\systemprofile\AppData%Windows%\System32\Tasks%Windows%\System32\wbem%Windows%\SysWOW64\WindowsPowerShell\v1.0%Windows%\SysWOW64\config\systemprofile\AppData%Windows%\SysWOW64\sysprep%Windows%\Scripts%Windows%\System%Windows%\Web%Users%
Important
The IOC scan tasks will not run / will fail on endpoints in the following situations:
The endpoint does not have a Windows operating system.
The endpoint's Bitdefender agent license is invalid.
The EDR module is not installed in the security agent installed on the target endpoints.
More than 100 Scan for IOC tasks are currently in queue.
Invalid data is entered by user in the IOC scan task configuration page.
Exchange scan
You can remotely scan the database of an Exchange Server by running an Exchange scan task.
To be able to scan the Exchange database, you must enable on-demand scanning by providing the credentials of an Exchange administrator. For more information, refer to Exchange Store Scanning.
To scan an Exchange Server database:
Go to the Network page.
Choose Computers and Virtual Machines from the views selector.
From the left-side pane, select the group containing the target Exchange Server. You can find the server displayed in the right-side pane.
Note
Optionally, you can apply filters to quickly find the target server:
Click the Filters menu and select the following options: Managed (Exchange Servers) from the Security tab and All items recursively from the Depth tab.
Enter the server's hostname or IP in the fields from the corresponding column headers.
Select the check box of the Exchange Server whose database you want to scan.
Click the Tasks button at the upper side of the table and choose Exchange scan. A configuration window will appear.
Configure the scan options:
General. Enter a suggestive name for the task.
For large databases, the scan task may take a long time and may impact the server performance. In such cases, select the check box Stop scan if it takes longer than and choose a convenient time interval from the corresponding menus.
policies.computers.exchange.antimalware.store.settings.target
policies.computers.exchange.antimalware.transport.rules.settings
policies.computers.exchange.antimalware.transport.rules.actions
Click Save to create the scan task. A confirmation message will appear.
You can view and manage the task on the Network > Tasks page. For more information, refer to Viewing and managing tasks.
Install agent
To protect your computers with the Bitdefender security agent, you must install it on each of them.
Important
In isolated networks that do not have direct connectivity with the GravityZone appliance, you can install the security agent with Relay role. In this case, the communication between the GravityZone appliance and the other security agents will be done through the Relay agent, which will also act as a local update server for security agents protecting the isolated network.
Once you have installed a Relay agent, it will automatically detect unprotected computers in the same network.
Note
It is recommended that the computer on which you install the Relay agent to be always on.
If no Relay agent is installed in the network, the detection of unprotected computers can be done manually by sending a Run network discovery task to a protected endpoint.
The Bitdefender protection can then be installed on computers remotely from Control Center.
Remote installation is performed in the background, without the user knowing about it.
Warning
Before installation, be sure to uninstall existing antimalware and firewall software from computers.
Installing the Bitdefender protection over existing security software may affect their operation and cause major problems with the system.
Windows Defender and Windows Firewall will be turned off automatically when installation starts.
If you want to deploy the security agent on a computer with Bitdefender Antivirus for Mac 5.X, you first must remove the latter manually. For the guiding steps, refer to Deploying Bitdefender Endpoint Security Tools on a machine with Bitdefender Antivirus for Mac.
When deploying the agent through a Linux Relay, the following conditions must be met:
The Relay endpoint must have installed the Samba package (
smbclient) version 4.1.0 or above and thenetbinary/command to deploy Windows agents.The
netbinary/command is usually delivered with the samba-client and / or samba-common packages. On some Linux distributions (such as CentOS 7.4), thenetcommand is only being installed when installing the full Samba suite (Common + Client + Server). Make sure that your Relay endpoint has thenetcommand available.Target Windows endpoints must have Administrative Share and Network Share enabled.
Target Linux and macOS endpoints must have SSH enabled and firewall disabled.
To run a remote installation task:
Connect and log in to Control Center.
Go to the Network page.
Choose Computers and Virtual Machines from the views selector.
Select the desired group from the left-side pane.
The entities contained in the selected group are displayed in the right-side pane table.
Optionally, you can apply filters to display unmanaged endpoints only. Click the Filters menu and select the following options: Unmanaged from the Security tab and All items recursively from the Depth tab.
Select the entities (endpoints or groups of endpoints) on which you want to install protection.
Click the
 Tasks button at the upper side of the table and choose Install agent.
Tasks button at the upper side of the table and choose Install agent.The Install agent task wizard is displayed.
Under Options section, configure the installation time:
Now, to launch the deployment immediately.
Scheduled, to set up the deployment recurrence interval. In this case, select the time interval that you want (hourly, daily or weekly) and configure it according to your needs.
For example, when certain operations are required on the target machine before installing the client (such as uninstalling other software and restarting the OS), you can schedule the deployment task to run every 2 hours. The task will start on each target machine every 2 hours until the deployment is successful.
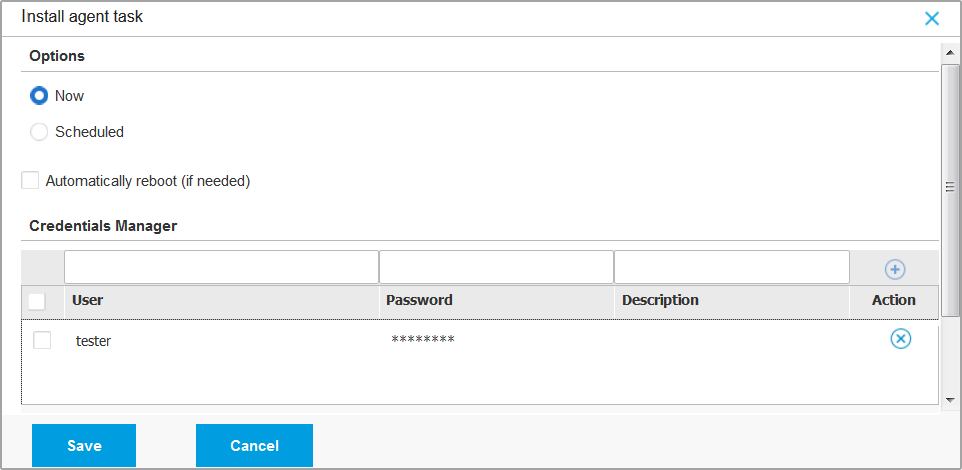
If you want target endpoints to automatically restart for completing the installation, select Automatically reboot (if needed).
Under the Credentials Manager section, specify the administrative credentials required for remote authentication on target endpoints. You can add the credentials by entering the user and password for each target operating system.
Important
For Windows 8.1 stations, you need to provide the credentials of the built-in administrator account or a domain administrator account. To learn more, refer to Client software deployment on Windows 8.1/10/2012 and above.
To add the required OS credentials:
Enter the user name and password of an administrator account in the corresponding fields from the table header.
If computers are in a domain, it suffices to enter the credentials of the domain administrator.
Use Windows conventions when entering the name of a user account:
For Active Directory machines use these syntaxes:
[email protected]anddomain\username. To make sure that entered credentials will work, add them in both forms ([email protected]anddomain\username).For Workgroup machines, it suffices to enter only the user name, without the workgroup name.
Optionally, you can add a description that will help you identify each account more easily.
Click the
 Add button. The account is added to the list of credentials.
Add button. The account is added to the list of credentials.Specified credentials are automatically saved to your Credentials Manager so that you do not have to enter them the next time. To access the Credentials Manager, just point to your username in the upper-right corner of the console.
Important
If the provided credentials are invalid, the client deployment will fail on the corresponding endpoints. Make sure to update the entered OS credentials in the Credentials Manager when these are changed on the target endpoints.
Select the check boxes corresponding to the accounts you want to use.
A warning message is displayed as long as you have not selected any credentials. This step is mandatory to remotely install the security agent on endpoints.
Under Deployer section, choose the entity to which the target endpoints will connect for installing and updating the client:
GravityZone Appliance, when endpoints connect directly to GravityZone Appliance.
In this case, you can also define:
A custom Communication Server by entering its IP or Hostname, if required.
Proxy settings, if target endpoints communicate with GravityZone Appliance via proxy. In this case, select Use proxy for communication and enter the required proxy settings in the fields below.
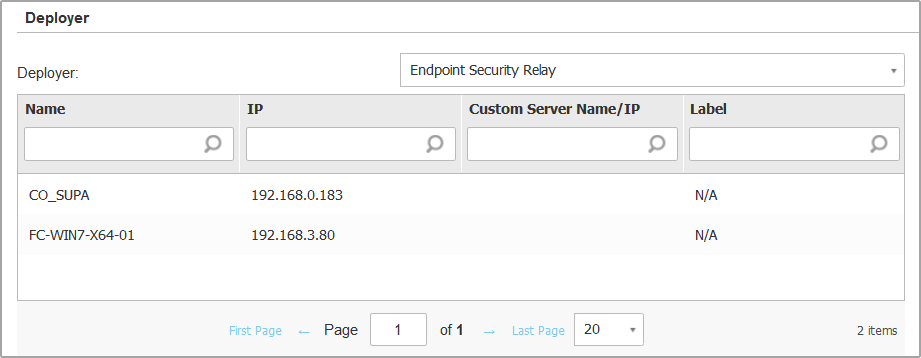
Endpoint Security Relay, if you want to connect the endpoints to a Relay client installed in your network. All machines with Relay role detected in your network will show-up in the table displayed below. Select the Relay machine that you want. Connected endpoints will communicate with Control Center only via the specified Relay.
Important
Port 7074 must be open, for the deployment through the Relay agent to work.
Use the Additional targets section if you want to deploy the client to specific machines from your network that are not shown in the network inventory. Expand the section and enter the IP addresses or hostnames of those machines in the dedicated field, separated by a comma. You can add as many IPs as you need.
You need to select one installation package for the current deployment. Click the Use package list and select the installation package that you want. You can find here all the installation packages previously created for your account and also the default installation package available with Control Center.
If needed, you can modify some of the selected installation package's settings by clicking the button Customize next to the Use package field.
The installation package's settings will appear below and you can make the changes that you need. To find out more about editing installation packages, refer to Create installation packages.
If you want to save the modifications as a new package, select the Save as package option placed at the bottom of the package settings list, and enter a name for the new installation package.
Click Save.
A confirmation message will appear.
You can view and manage the task in the Network > Tasks page.
If using VMware Horizon View Persona Management, it is recommended to configure Active Directory Group Policy to exclude the following Bitdefender processes (without the full path):
bdredline.exeepconsole.exeepintegrationservice.exeepprotectedservice.exeepsecurityservice.exeepupdateservice.exeepupdateserver.exe
These exclusions must apply as long as the security agent runs on endpoint. For details, refer to this VMware Horizon documentation page.
Uninstall agent
To remotely uninstall the Bitdefender protection:
Go to the Network page.
Choose Computers and Virtual Machines from the views selector.
Select the container that you want from the left-side pane. All computers from the selected container are displayed in the right-side pane table.
Select the check boxes of computers from which you want uninstall the Bitdefender security agent.
Click the
 Tasks button at the upper side of the table and choose Uninstall agent.
Tasks button at the upper side of the table and choose Uninstall agent.A configuration window is displayed, allowing you to opt for keeping the quarantined items on the client machine.
Click Save to create the task. A confirmation message will appear.
You can view and manage the task on the Network > Tasks page. For more information, refer to Viewing and managing tasks.
Note
If you want to reinstall protection, be sure to restart the computer first.
Watch a full video tutorial on the topic here:
Update agent
Check the status of managed computers periodically. If you notice a computer with security issues, click its name to display the Information page. For more information, refer to Checking the computers status .
Outdated clients or outdated security content represent security issues. In these cases, you should run an update on the corresponding computer. This task can be done locally from the computer, or remotely from Control Center.
To remotely update the client and the security content on managed computers:
Go to the Network page.
Choose Computers and Virtual Machines from the views selector.
Select the container that you want from the left-side pane. All computers from the selected container are displayed in the right-side pane table.
Select the check boxes of computers where you want to run a client update.
Click the
 Tasks button at the upper side of the table and choose Update agent. A configuration window will appear.
Tasks button at the upper side of the table and choose Update agent. A configuration window will appear.You can choose to update only the product, only the security content or both.
Click Update to run the task. A confirmation message will appear.
You can view and manage the task on the Network > Tasks page. For more information, refer to Viewing and managing tasks.
Upgrade agent
This task is available only when Endpoint Security agent is installed and detected in the network. Bitdefender recommends upgrading from Endpoint Security to Bitdefender Endpoint Security Tools Bitdefender Endpoint Security Tools, for a last-generation endpoint protection.
To easily find the security agents that are not upgraded, you can generate an upgrade status report. For details about how to create reports, refer to Creating reports.
Reconfigure agent
The security agent's protection modules, roles and scanning modes are initially configured within the installation package. After you have installed the security agent in your network, you can anytime change the initial settings by sending a Reconfigure agent remote task to the managed endpoints you are interested in.
Warning
The Reconfigure agent task overwrites all installation settings and none of the initial settings is kept. While using this task, make sure to reconfigure all the installation settings for the target endpoints.
You can change the installation settings from the Network area or from the Endpoint Modules Status report.
To change the installation settings for one or several endpoints:
Go to the Network page.
Choose Computers and Virtual Machines from the views selector.
Select the group that you want from the left-side pane. All computers from the selected container are displayed in the right-side pane table.
Select the check boxes of computers for which you want to change the installation settings.
Click the
 Tasks button at the upper side of the table and choose Reconfigure agent.
Tasks button at the upper side of the table and choose Reconfigure agent.Note
The Reconfigure agent page will not show which modules are currently installed on the endpoint.
Select one of the actions below:
Add - Add new modules besides the existing ones.
Remove - Remove specific modules from the existing ones.
Note
The Show all modules option enables Admins/Partners to conveniently access and view all modules, regardless of any licence restrictions that may be in place.
You can uninstall modules that were previously installed but have become unusable or invisible due to licence changes or downgrades. This information is specific to the Remove option within the Reconfigure agent task.
Match list - Match the modules installed with your selection.
Note
Any unselected modules will be removed.
Under Scan mode select the scan mode to be used on the endpoint:
Note
Only available when selecting the Match List option.
The Scan mode option becomes available only when the selected endpoints belong to the same company and the Detection and prevention operation mode is chosen. If endpoints from different companies are selected, the Scan Mode section will not be visible.
Automatic. In this case, the security agent will automatically detect the endpoint's configuration and will adapt the scanning technology accordingly:
Central Scan in Public or Private Cloud (with Security Server) with fallback on Hybrid Scan (Light Engines), for physical endpoints with low hardware performance and for virtual machines. This case requires at least one Security Server deployed in the network.
Local Scan (with Full Engines) for physical endpoints with high hardware performance.
Local scan for EC2 instances and Microsoft Azure virtual machines.
Note
Low performance endpoints are considered to have the CPU frequency less than 1.5 GHz, or RAM memory less than 1 GB.
Custom. In this case, you can configure the scan mode by choosing between several scanning technologies for physical and virtual machines:
Central Scan in Public or Private Cloud (with Security Server), which can fallback* on Local Scan (with Full Engines) or on Hybrid Scan (with Light Engines)
Hybrid Scan (with Light Engines)
Local Scan (with Full Engines)
Default scan modes:
The default scan mode for EC2 instances is Local Scan (security content is stored on the installed security agent, and the scan is run locally on the machine). If you want to scan your EC2 instances with a Security Server, you need to configure the security agent’s installation package and the applied policy accordingly.
Note
In this case, the BitdefenderSecurity Server hosted in the AWS region corresponding to the target EC2 instances is automatically assigned.
The default scan mode for Microsoft Azure virtual machines is Local Scan (security content is stored on the installed security agent, and the scan is run locally on the machine). If you want to scan your Microsoft Azure virtual machines with a Security Server, you need to configure the security agent’s installation package and the applied policy accordingly.
The default scan mode for BEST for Linux v7 when using the Bitdefender for Security Containers add-on is:
Hybrid Scan, for physical endpoints (including container hosts) and nodes (in case of Kubernetes).
Central Scan with the fallback on Hybrid Scan for endpoints (including container hosts) and nodes (in case of Kubernetes) that are either virtual machines or on a cloud infrastructure (whether IaaS or PaaS) supported by GravityZone integrations.
Note
A Security Server needs to be available for this scan to apply. If none is available the scan mode will be set to Hybrid.
For more information regarding available scanning technologies, refer to Antimalware.
Security Server Assignment.
Click the Security Server list in the table header. The list of detected Security Servers is displayed.
Select an entity.
Click the
 Add button from the Actions column header.
Add button from the Actions column header.The Security Server is added to the list.
Follow the same steps to add several security servers, if available. In this case, you can configure their priority using the
 up and
up and  down arrows available at the right side of each entity. When the first Security Server is unavailable, the next one will be used and so on.
down arrows available at the right side of each entity. When the first Security Server is unavailable, the next one will be used and so on.To delete one entity from the list, click the corresponding
 Delete button at the upper side of the table.
Delete button at the upper side of the table.
You can choose to encrypt the connection to Security Server by selecting the Use SSL option.
Under the Scheduler section, configure the time when the task will run:
Now, to launch the task immediately.
Scheduled, to set up the task recurrence interval. In this case, select the time interval that you want (hourly, daily or weekly) and configure it according to your needs.
For example, when other important processes are also required to run on the target machine, you can schedule the task to run every 2 hours. The task will start on each target machine every 2 hours until it is successfully done.
Configure the modules, roles and scan modes for the target endpoint as you want. For more information, refer to Install security agents - standard procedure
Note
You can only modify scan modes by using the Match list action.
Warning
Only the supported modules for each operating system will be installed.
The Firewall module is available only for supported Windows workstations.
Click Save. A confirmation message will appear.
You can view and manage the task on the Network > Tasks page. For more information, refer to Viewing and managing tasks.
Repair agent
Use the Repair agent task as an initial troubleshooting task for any number of endpoint issues. The task downloads the latest install package on the target endpoint and then performs a reinstall of the agent.
Note
The modules currently configured on the agent will not be changed.
The repair task will reset the security agent to the version published in the Configuration > Update > Components page.
To send a Repair agent task to the client:
Go to the Network page.
Choose Virtual machines from the views selector.
Select the container that you want from the left-side pane.
All computers from the selected container are displayed in the right-side pane table.
Select the check boxes of computers where you want to run a client repair.
Click the
 Tasks button and choose Repair agent.
Tasks button and choose Repair agent.A confirmation window will appear.
Select the I understand and agree check box and click the Save button to run the task.
Note
To finish the repair task, a client restart might be required.
You can view and manage the task on the Network > Tasks page. For more, information refer to Viewing and managing tasks.
Restart endpoint
You can choose to remotely restart managed computers.
Note
Check the Network > Tasks page before restarting certain computers. Previously created tasks may still be processing on target computers.
This task is available only for distributed environments.
Go to the Network page.
Choose Computers and Virtual Machines from the views selector.
Select the container that you want from the left-side pane. All computers from the selected container are displayed in the right-side pane table.
Select the check boxes of computers you want to restart.
Click the
 Tasks button at the upper side of the table and choose Restart endpoint.
Tasks button at the upper side of the table and choose Restart endpoint.Choose the restart schedule option:
Select Restart now to restart computers immediately.
Select Restart on and use the fields below to schedule the restart at the desired date and time.
Click Save. A confirmation message will appear.
You can view and manage the task on the Network > Tasks page. For more information, refer to Viewing and managing tasks.
Isolate endpoint
Isolate an endpoint in order to contain the spreading of potentially malicious activities, such as Lateral movement, to other endpoints in your network. When an endpoint is isolated, it can only communicate with GravityZone.
To isolate an endpoint:
Go to the Network page.
Select the container that you want from the left side pane. All endpoints from the selected container are displayed in the right side grid.
Select the checkbox of the endpoint you want to isolate.
Click the
 Tasks button at the upper side of the table and choose Isolate endpoint.
Tasks button at the upper side of the table and choose Isolate endpoint.Confirm your choice.
You can view and manage the task on the Network > Tasks page. For more information, refer to Viewing and managing tasks.
Isolated endpoints will also display a warning message in the General tab of the endpoint's Information window.
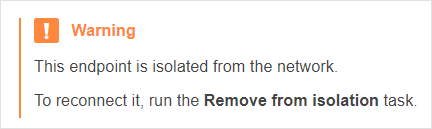
Note
For the Isolate endpoint option to be available, Customer companies require at least one of the products below:
GravityZone Business Security Premium
GravityZone Business Security Enterprise
GravityZone Security for Workstations
GravityZone Security for Servers
GravityZone EDR Cloud
GravityZone Security for Endpoints Physical Workstations
GravityZone Security for Endpoints Physical Servers
GravityZone Security for Endpoints Virtualized Environments VDI
GravityZone Security for Endpoints Virtualized Environments VS
GravityZone Security for Virtual Env per CPU
Security for AWS
If Customer companies have a Monthly subscription plan, they need to have Advanced Threat Security enabled.
Remove from isolation
To remove an endpoint from isolation and bring it back on the network:
Go to the Network page.
Select the container that you want from the left side pane. All endpoints from the selected container are displayed in the right side grid.
Select the checkbox of the endpoint you want to remove from isolation.
Click the
 Tasks button at the upper side of the table and choose Remove from isolation.
Tasks button at the upper side of the table and choose Remove from isolation.Confirm your choice.
Note
For the Isolate option to be available, Customer companies require at least one of the products below:
GravityZone Business Security Premium
GravityZone Business Security Enterprise
GravityZone Security for Workstations
GravityZone Security for Servers
GravityZone EDR Cloud
GravityZone Security for Endpoints Physical Workstations (version released in April 2022)
GravityZone Security for Endpoints Physical Servers (version released in April 2022)
GravityZone Security for Endpoints Virtualized Environments VDI (version released in April 2022)
GravityZone Security for Endpoints Virtualized Environments VS (version released in April 2022)
GravityZone Security for Virtual Env per CPU (version released in April 2022)
Security for AWS
If Customer companies have a Monthly subscription plan, they need to have Advanced Threat Security enabled.
Run network discovery
Network discovery is done automatically by security agents with Relay role. If you do not have a Relay agent installed in your network, you have to manually send a network discovery task from a protected endpoint.
To run a network discovery task in your network:
Go to the Network page.
Choose Computers and Virtual Machines from the views selector.
Select the container that you want from the left-side pane. All computers from the selected container are displayed in the right-side pane table.
Select the check box of the computer you want to perform network discovery with.
Click the
 Tasks button at the upper side of the table and choose Run network discovery.
Tasks button at the upper side of the table and choose Run network discovery.A confirmation message will appear. Click Yes.
You can view and manage the task on the Network > Tasks page. For more information, refer to Viewing and managing tasks.
Run applications discovery
When the Application Control module is activated for the first time on an endpoint, the application discovery process will start in the background. Any future changes made in the policy for this module will not trigger the discovery process again.
To discover applications in your network:
Go to the Network page.
Choose Computers and Virtual Machines from the views selector.
Select the group that you want from the left-side pane. All computers from the selected container are displayed in the right-side pane table.
Select the computers on which you want to perform applications discovery.
Click the
 Tasks button at the upper side of the table and choose Run applications discovery.
Tasks button at the upper side of the table and choose Run applications discovery.Note
Bitdefender Endpoint Security Tools with Application Control must be installed and activated on the selected computers. Otherwise, the task will be grayed out. When a selected group contains both valid and invalid targets, the task will be sent out only to valid endpoints.
Click Yes in the confirmation window to proceed.
The discovered applications and processes are displayed on the Network > Application Inventory page. For more information, refer to Application inventory.
Note
The Run applications discovery task may take a while, depending on the number of applications installed. You can view and manage the task on the Network > Tasks page. For more information, refer to Viewing and managing tasks.
Update Security Server
Installed Security Server can be viewed and managed also from Computers and Virtual Machines, under the Custom Groups folder.
If a Security Server is outdated, you can send it an update task:
Go to the Network page.
Choose Computers and Virtual Machines from the views selector.
Select the group where the Security Server is installed.
To easily locate the Security Server, you can use the Filters menu as follows:
Go to Security tab and select Security Servers only.
Go to Depth tab and select All items recursively.
Click the
 Tasks button at the upper side of the table and choose Update Security Server.
Tasks button at the upper side of the table and choose Update Security Server.Choose the type of update to perform:
Security features, for installing the Bitdefender new features, improvements and fixes, and security fixes
Operating system, for upgrading the operating system of the Security Server appliance
Note
Check the release notes to find out what type of update you are going to deploy.
Additionally, for the operating system update, select the time and date when the update should run. You can run it immediately or schedule it at a convenient time, such as a maintenance window.
Click OK to create the task.
You can view and manage the task on the Network > Tasks page. For more information, refer to Viewing and Managing Tasks.
Important
It is recommended to use this method to update the Security Server for NSX, otherwise you will lose the quarantine saved on the appliance.
Running tasks on virtual machines
From the Network page, you can remotely run a number of administrative tasks on virtual machines.
This is the list of tasks you can run:
You can choose to create tasks individually for each virtual machine or for groups of virtual machines. For example, you can remotely install Bitdefender Endpoint Security Tools on a group of unmanaged virtual machines. At a later time, you can create a scan task for a certain virtual machine from the same group.
For each virtual machine, you can only run compatible tasks. For example, if you select an unmanaged virtual machine, you can only choose to install the security agent, all the other tasks being disabled.
For a group, the selected task will be created only for compatible virtual machines. If none of the virtual machines in the group is compatible with the selected task, you will be notified that the task could not be created.
Once created, the task will start running immediately on online virtual machines. If a virtual machine is offline, the task will run as soon as it gets back online.
You can view and manage the task in the Network > Tasks page. For more information, refer to Viewing and managing tasks.
Malware scan
To remotely run a scan task on one or several virtual machines:
Go to the Network page.
Choose Virtual Machines from the views selector.
Select the container that you want from the left-side pane.
All the entities contained in the selected group are displayed in the right-side pane table.
Select the check boxes corresponding to the objects you want to scan.
Click the
 Tasks button at the upper side of the table and choose Malware scan. A configuration window will appear.
Tasks button at the upper side of the table and choose Malware scan. A configuration window will appear.Configure the scan options:
Go to the Options tab to set the scan options.
Click the security level that best suits your needs (Aggressive, Normal or Permissive).
Use the description on the right-side of the scale to guide your choice.
Based on the selected profile, the scan options in the Settings section are automatically configured. However, if you want to, you can configure them in detail. To do that, select the Custom option and then expand the Settings section.

The following options are available:
File Types
Use these options to specify which types of files you want to be scanned.
You can set the security agent to scan all files (regardless of their file extension), application files only or specific file extensions you consider to be dangerous.
Scanning all files provides best protection, while scanning applications only can be used to perform a quicker scan.
Note
Application files are far more vulnerable to malware attacks than other types of files.
For more information, refer to Application file types.
If you want only specific extensions to be scanned, choose Custom extensions from the menu and then enter the extensions in the edit field, pressing
Enterafter each extension.Note
Bitdefender security agents installed on Windows and Linux operating systems scan most of the .ISO formats, but does not take any action on them.

Archives
Archives containing infected files are not an immediate threat to system security.
The malware can affect the system only if the infected file is extracted from the archive and executed without having real-time protection enabled.
However, it is recommended to scan archives in order to detect and remove any potential threat, even if it is not an immediate threat.
Important
Scanning archived files increases the overall scanning time and requires more system resources.
Scan inside archives
Select this option if you want to check archived files for malware.
If you decide on using this option, you can configure the following optimization options:
Limit archive size to (MB)
You can set a maximum accepted size limit of archives to be scanned.
Select the corresponding check box and type the maximum archive size (in MB).
Maximum archive depth (levels)
Select the corresponding check box and choose the maximum archive depth from the menu.
For best performance choose the lowest value, for maximum protection choose the highest value.
Scan email archives
Select this option if you want to enable scanning of email message files and email databases, including file formats such as .eml, .msg, .pst, .dbx, .mbx, .tbb and others.
Important
Email archive scanning is resource intensive and can impact system performance.
Miscellaneous
Select the corresponding check boxes to enable the desired scan options.
Scan boot sectors
Scans the system’s boot sector.
This sector of the hard disk contains the necessary virtual machine code to start the boot process.
When a virus infects the boot sector, the drive may become inaccessible and you may not be able to start your system and access your data.
Scan registry
Select this option to scan registry keys.
Windows Registry is a database that stores configuration settings and options for the Windows operating system components, as well as for installed applications.
Scan for rootkits
Select this option to scan for glossary.rootkit rootkits and objects hidden using such software.
Scan for keyloggers
Select this option to scan for glossary.keylogger keylogger software.
Keyloggers are not malicious applications in nature, but they can be used with malicious intent.
The hacker can find out sensitive information from the stolen data, such as bank account numbers and passwords, and use it to gain personal benefits.
Scan memory
Select this option to scan programs running in the system's memory.
Scan cookies
Select this option to scan the cookies stored by browsers on the virtual machine.
Scan only new and changed files
By scanning only new and changed files, you may greatly improve overall system responsiveness with a minimum trade-off in security.
Scan for Potentially Unwanted Applications (PUA)
A Potentially Unwanted Application (PUA) is a program that may be unwanted on the PC and sometimes comes bundled with freeware software. Such programs can be installed without the user's consent (also called adware) or will be included by default in the express installation kit (ad-supported). Potential effects of these programs include the display of pop-ups, installing unwanted toolbars in the default browser or running several processes in the background and slowing down the PC performance.
Scan detachable volumes
Select this option to scan any removable storage drive attached to the virtual machine.
Actions
Depending on the type of detected file, the following actions are taken automatically:
When an infected file is found
Bitdefender detects files as infected through various advanced mechanisms, which include malware signatures, machine learning and artificial intelligence (AI) based technologies.
The Bitdefender security agent can normally remove the malware code from an infected file and reconstruct the original file. This operation is known as disinfection.
If an infected file is detected, the Bitdefender security agent will automatically attempt to disinfect it.
If disinfection fails, the file is moved to quarantine in order to contain the infection.
Important
For particular types of malware, disinfection is not possible because the detected file is entirely malicious. In such cases, the infected file is deleted from the disk.
When a suspect file is found
Files are detected as suspicious by the heuristic analysis and other Bitdefender technologies.
These provide a high detection rate, but the users must be aware of certain false positives (clean files detected as suspicious) in some cases.
Suspect files cannot be disinfected, because no disinfection routine is available.
Scan tasks are configured by default to ignore suspect files.
You may want to change the default action in order to move suspect files to quarantine.
Quarantined files are sent for analysis to Bitdefender Labs on a regular basis.
If malware presence is confirmed, a signature is released to allow removing the malware.
When a rootkit is found
Rootkits represent specialized software used to hide files from the operating system.
Though not malicious in nature, rootkits are often used to hide malware or to conceal the presence of an intruder into the system.
Detected rootkits and hidden files are ignored by default.
When a virus is found on an NSX virtual machine, the Security Server automatically tags the virtual machine with a Security Tag, provided this options has been selected at vCenter Server integration.
For this purpose, the NSX includes three security tags, specific to the threat severity:
ANTI_VIRUS.VirusFound.threat=low, applying on machine when Bitdefender finds low risk malware, which it can delete.ANTI_VIRUS.VirusFound.threat=medium, applying on the machine if Bitdefender cannot delete the infected files, but instead it disinfects them.ANTI_VIRUS.VirusFound.threat=high, applying on the machine if Bitdefender can neither delete, nor disinfect the infected files, but blocks access to them.
You can isolate infected machines by creating a security groups with dynamic membership based on the security tags.
Important
If Bitdefender finds on a machine threats of different severity levels, it will apply all matching tags.
A security tag is removed from a machine only after a Full Scan is performed and the machine has been disinfected.
Though not recommended, you can change the default actions.
You can specify a second action to be taken if the first one fails and different actions for each category.
Choose from the corresponding menus the first and the second action to be taken on each type of detected file.
The following actions are available:
Disinfect
Remove the malware code from infected files.
It is recommended to always keep this as the first action to be taken on infected files.
Move files to quarantine
Move detected files from their current location to the quarantine folder.
Quarantined files cannot be executed or opened; therefore, the risk of getting infected disappears.
You can manage quarantine files from the quarantine.....Quarantine page of the console.
Delete
Delete detected files from the disk, without any warning.
It is advisable to avoid using this action.
Ignore
No action will be taken on detected files. These files will only appear in the scan log.
Go to Target tab to add the locations you want to be scanned on the target virtual machines.
In the Scan target section you can add a new file or folder to be scanned:
Choose a predefined location from the drop-down menu or enter the Specific paths you want to scan.
Specify the path to the object to be scanned in the edit field.
If you have chosen a predefined location, complete the path as needed.
For example, to scan the entire
Program Filesfolder, it suffices to select the corresponding predefined location from the drop-down menu.To scan a specific folder from
Program Files, you must complete the path by adding a backslash (\) and the folder name.If you have chosen Specific paths, enter the full path to the object to be scanned.
It is advisable to use system variables (where appropriate) to make sure the path is valid on all target virtual machines. For more information regarding system variables, refer to System variables.
Click the corresponding
 Add button.
Add button.
To edit an existing location, click it.
To remove a location from the list, click the corresponding
 Delete button.
Delete button.For network scan tasks, you need to enter the credentials of a user account with read/write permissions on the target network drives, for the security agent to be able to access and take actions on these network drives.
Click the Exclusions section if you want to define target exclusions.

You can either use the exclusions defined by policy or define explicit exclusions for the current scan task.
For more details regarding exclusions, refer to Exclusions .
Click Save to create the scan task. A confirmation message will appear.
You can view and manage the task on the Network > Tasks page. For more information, refer to Viewing and managing tasks.
Note
To schedule a scan task, go to the Policies vage, select the policy assigned to the virtual machines you are interested in, and add a scan task in the Antimalware > On-Demand section. For more information, refer to On-Demand.
Patch tasks
It is recommended to regularly check for software updates and apply them as soon as possible. GravityZone automates this process through security policies, but if you need to update the software on certain virtual machines right away, run the following tasks in this order:
Prerequisites
The security agent with Patch Management module is installed on target machines.
For the scanning and installation tasks to be successful, Windows machines must meet these conditions:
Trusted Root Certification Authorities stores the DigiCert Trusted Root G4 certificate.
Intermediate Certification Authorities includes the DigiCert Trusted G4 Code Signing RSA4096 SHA384 2021 CA1.
Endpoints have installed the patches mentioned in these Microsoft articles:
For Windows 7 and Windows Server 2008 R2: Microsoft Security Advisory 3033929
For Windows Vista and Windows Server 2008: You cannot run an application that is signed with a SHA-256 certificate on a computer that is running Windows Vista SP2 or Windows Server 2008 SP2
Patch scan
Virtual machines with outdated software are vulnerable to attacks. It is recommended to regularly check the software installed on your machines and update it as soon as possible. To scan your virtual machines for missing patches:
Go to the Network page.
Choose Virtual Machines from the views selector.
Select the container that you want from the left-side pane. All endpoints from the selected container are displayed in the right-side pane table.
Select the target endpoints.
Click the
 Tasks button at the upper side of the table and choose Patch Scan. A confirmation window will appear.
Tasks button at the upper side of the table and choose Patch Scan. A confirmation window will appear.Click Yes to confirm the scan task.
When the task finishes, GravityZone adds in Patch Inventory all patches your software needs. For more details, refer to Patch inventory.
Note
To schedule patch scanning, edit the policies assigned to the target machines, and configure the settings in the Patch Management section. For more information, refer to Patch management.
Patch install
To install one or more patches on the target virtual machines:
Go to the Network page.
Choose Virtual Machines from the views selector.
Select the container that you want from the left-side pane. All endpoints from the selected container are displayed in the right-side pane table.
Click the
 Tasks button at the upper side of the table and choose Patch Install.
Tasks button at the upper side of the table and choose Patch Install.A configuration window will appear. Here, you can view all patches missing from the target virtual machines.
If needed, use the sorting and filtering options at the upper side of the table to find specific patches.
Click the
 Columns button at the upper-right side of the pane to view only relevant information.
Columns button at the upper-right side of the pane to view only relevant information.Select the patches you want to install.
Certain patches depend on others. In such case, they are automatically selected once with the patch.
Clicking the numbers of CVEs or Products will display a pane in the left side. The pane contains additional information, such as the CVEs which the patch resolves, or the products to which the patch applies. When done reading, click Close to hide the pane.
Select Reboot endpoints after installing the patch, if required to restart the endpoints immediately after the patch installation, if a system restart is required. Take into account that this action may disrupt the user activity.
Click Install.
The installation task is created, together with sub-tasks for each target virtual machines.
You can view and manage the task on the Network > Tasks page. For more information, refer to Viewing and managing tasks.
Note
To schedule patch deployment, edit the policies assigned to the target machines, and configure the settings in the Patch Management section. For more information, refer to Patch management.
You can also install a patch from the Patch Inventory page, starting from a certain patch that you are interested in. In this case, select the patch from the list, click the Install button at the upper side of the table and configure the patch installation details. For more details, refer to Patch inventory.
After installing a patch, we recommend sending a Patch scan task to target endpoints. This action will update the patch information stored in GravityZone for your managed networks.
You can uninstall patches:
Remotely, by sending a patch uninstall task from GravityZone.
Locally on the machine. In this case, you need to log in as an administrator to the endpoint and run the uninstaller manually.
Exchange scan
You can remotely scan the database of an Exchange Server by running an Exchange scan task.
To be able to scan the Exchange database, you must enable on-demand scanning by providing the credentials of an Exchange administrator. For more information, refer to Antimalware.
To scan an Exchange Server database:
Go to the Network page.
Choose Virtual Machines from the views selector.
From the left-side pane, select the group containing the target Exchange Server. You can find the server displayed in the right-side pane.
Note
Optionally, you can apply filters to quickly find the target server:
Click the Filters menu and select the following options: Managed (Exchange Servers) from the Security tab and All items recursively from the Depth tab.
Enter the server's hostname or IP in the fields from the corresponding column headers.
Select the check box of the Exchange Server whose database you want to scan.
Click the Tasks button at the upper side of the table and choose Exchange scan. A configuration window will appear.
Configure the scan options:
General. Enter a suggestive name for the task.
For large databases, the scan task may take a long time and may impact the server performance. In such cases, select the check box Stop scan if it takes longer than and choose a convenient time interval from the corresponding menus.
Target. Select the containers and objects to be scanned. You can choose to scan mailboxes, public folders or both. Beside emails, you can choose to scan other objects such as Contacts, Tasks, Appointments and Post items. You can furthermore set the following restrictions to the content to be scanned:
Only unread messages
Only items with attachments
Only new items, received in a specified time interval
For example, you can choose to scan only emails from user mailboxes, received in the last seven days.
Select the Exclusions check box, if you want to define scan exceptions. To create an exception, use the fields from the table header as follows:
Select the repository type from the menu.
Depending on the repository type, specify the object to be excluded:
Repository type
Object format
Mailbox
Email address
Public Folder
Folder path, starting from the root
Database
The database identity
Note
To obtain the database identity, use the Exchange shell command:
Get-MailboxDatabase | fl name,identityYou can enter only one item at a time. If you have several items of the same type, you must define as many rules as the number of items.
Click the
 Add button at the upper side of the table to save the exception and add it to the list.
Add button at the upper side of the table to save the exception and add it to the list.
To remove an exception rule from the list, click the corresponding
 Delete button.
Delete button.Options. Configure the scan options for emails matching the rule:
Scanned file types. Use this option to specify which file types you want to be scanned. You can choose to scan all files (regardless of their file extension), application files only, or specific file extensions you consider to be dangerous. Scanning all files provides the best protection, while scanning only applications is recommended for a quicker scan.
Note
Application files are far more vulnerable to malware attacks than other types of files. For more information, refer to Application file types.
If you want to scan only files with specific extensions, you have two alternatives:
User defined extensions, where you must provide only the extensions to be scanned.
All files, except specific extensions, where you must enter only the extensions to be skipped from scanning.
Attachment / email body maximum size (MB). Select this check box and enter a value in the corresponding field to set the maximum accepted size of an attached file or of the email body to be scanned.
Archive maximum depth (levels). Select the check box and choose the maximum archive depth from the corresponding field. The lower the depth level is, the higher the performance and the lower the protection grade.
Scan for Potentially Unwanted Applications (PUA). Select this check box to scan for possibly malicious or unwanted applications, such as adware, which may install on systems without user’s consent, change the behavior of various software products and lower the system performance.
Actions. You can specify different actions for the security agent to automatically take on files, based on the detection type.
The detection type separates the files into three categories:
Infected files. Bitdefender detects files as infected through various advanced mechanisms, which include malware signatures, machine learning and artificial intelligence (AI) based technologies.
Suspect files. These files are detected as suspicious by the heuristic analysis and other Bitdefender technologies. These provide a high detection rate, but the users must be aware of certain false positives (clean files detected as suspicious) in some cases.
Unscannable files. These files cannot be scanned. Unscannable files include but are not limited to password-protected, encrypted or over-compressed files.
For each detection type, you have a default or main action and an alternative action in case the main one fails. Though not recommended, you can change these actions from the corresponding menus. Choose the action to be taken:
Disinfect. Removes the malware code from infected files and reconstructs the original file. For particular types of malware, disinfection is not possible because the detected file is entirely malicious. It is recommended to always keep this as the first action to be taken on infected files. Suspect files cannot be disinfected, because no disinfection routine is available.
Reject / Delete email. The email is deleted without any warning. It is advisable to avoid using this action.
Delete file. Deletes the attachments with issues without any warning. It is advisable to avoid using this action.
Replace file. Deletes the files with issues and inserts a text file that notifies the user of the actions taken.
Move file to quarantine. Moves detected files to the quarantine folder and inserts a text file that notifies the user of the actions taken. Quarantined files cannot be executed or opened; therefore, the risk of getting infected disappears. You can manage quarantine files from the Quarantine page.
Note
Please note that the quarantine for Exchange Servers requires additional hard-disk space on the partition where the security agent is installed. The quarantine size depends on the number and size of the emails stored.
Take no action. No action will be taken on detected files. These files will only appear in the scan log. Scan tasks are configured by default to ignore suspect files. You may want to change the default action in order to move suspect files to quarantine.
By default, when an email matches the rule scope, it is processed exclusively in accordance with the rule, without being checked against any other remaining rule. If you want to continue checking against the other rules, clear the check box If the rule conditions are matched, stop processing more rules.
Click Save to create the scan task. A confirmation message will appear.
You can view and manage the task on the Network > Tasks page. For more information, refer to Viewing and Managing Tasks .
Install agent
To protect your virtual machines with Bitdefender Endpoint Security Tools Relay, you must install Bitdefender security agent on each of them.
Bitdefender security agent manages protection on the virtual machines. It also communicates with Control Center to receive the administrator's commands and to send the results of its actions.
Once you have installed a Bitdefender security agent in a network, it will automatically detect unprotected virtual machines in that network.
The Bitdefender Endpoint Security Tools Relay protection can then be installed on those virtual machines remotely from Control Center.
Remote installation is performed in the background, without the user knowing about it.
In isolated networks that do not have direct connectivity with the GravityZone appliance, you can install the security agent with Relay role. In this case, the communication between the GravityZone appliance and the other security agents will be done through the Relay agent, which will also act as a local update server for security agents protecting the isolated network.
Note
It is recommended that the machine on which you install the Relay agent to be always on.
Warning
Before installation, be sure to uninstall existing antimalware and firewall software from virtual machines.
Installing the Bitdefender protection over existing security software may affect their operation and cause major problems with the system.
Windows Defender and Windows Firewall will be turned off automatically when installation starts.
To remotely install the Bitdefender Endpoint Security Tools Relay protection on one or several virtual machines:
Connect and log in to Control Center.
Go to the Network page.
Choose Virtual Machines from the views selector.
Select the container that you want from the left-side pane.
The entities contained in the selected group are displayed in the right-side pane table.
Optionally, you can apply filters to display unmanaged machines only. Click the Filters menu and select the following options: Unmanaged from the Security tab and All items recursively from the Depth tab.
Select the entities (virtual machines, hosts, clusters or groups) on which you want to install protection.
Click the
 Tasks button at the upper side of the table and choose Install agent.
Tasks button at the upper side of the table and choose Install agent.The Install agent task wizard is displayed.

Under Options section, configure the installation time:
Now, to launch the deployment immediately.
Scheduled, to set up the deployment recurrence interval. In this case, select the time interval that you want (hourly, daily or weekly) and configure it according to your needs.
For example, when certain operations are required on the target machine before installing the client (such as uninstalling other software and restarting the OS), you can schedule the deployment task to run every 2 hours. The task will start on each target machine every 2 hours until the deployment is successful.
If you want target endpoints to automatically restart for completing the installation, select Automatically reboot (if needed).
Under the Credentials Manager section, specify the administrative credentials required for remote authentication on target endpoints. You can add the credentials by entering the user and password for each target operating system.
Important
For Windows 8.1 stations, you need to provide the credentials of the built-in administrator account or a domain administrator account. To learn more, refer to Client software deployment on Windows 8.1/10/2012 and above.
Note
A warning message is displayed as long as you have not selected any credentials. This step is mandatory to remotely install Bitdefender Endpoint Security Tools on endpoints.
To add the required OS credentials:
Enter the user name and password of an administrator account for each target operating system in the corresponding fields from the credentials table header. Optionally, you can add a description that will help you identify each account more easily.
If the machines are in a domain, it suffices to enter the credentials of the domain administrator.
Use Windows conventions when entering the name of a user account:
For Active Directory machines use these syntaxes:
[email protected]anddomain\username. To make sure that entered credentials will work, add them in both forms ([email protected]anddomain\username).For Workgroup machines, it suffices to enter only the user name, without the workgroup name.
Click the
 Add button.
Add button.The account is added to the list of credentials.
Specified credentials are automatically saved to your Credentials Manager so that you do not have to enter them the next time. To access the Credentials Manager, just click to your username in the upper-right corner of the console.
Important
If the provided credentials are invalid, the client deployment will fail on the corresponding endpoints. Make sure to update the entered OS credentials in the Credentials Manager when these are changed on the target endpoints.
Select the check boxes corresponding to the accounts you want to use.
Under Deployer section, choose the entity to which the target machines will connect for installing and updating the client:
GravityZone Appliance, when the machines connect directly to GravityZone Appliance.
For this case, you can also define a custom Communication Server by entering its IP or Hostname, if required.
Endpoint Security Relay, if you want to connect the machines to a Relay client installed in your network. All machines with Relay role detected in your network will show-up in the table displayed below. Select the Relay machine that you want. Connected endpoints will communicate with Control Center only via the specified Relay.
Important
Port 7074 must be open, for the deployment through the Relay agent to work.
When deploying the agent through a Linux Relay, the following conditions must be met:
The Relay endpoint must have installed the Samba package (
smbclient) version 4.1.0 or above and thenetbinary/command to deploy Windows agents.The
netbinary/command is usually delivered with the samba-client and / or samba-common packages. On some Linux distributions (such as CentOS 7.4), thenetcommand is only being installed when installing the full Samba suite (Common + Client + Server). Make sure that your Relay endpoint has thenetcommand available.Target Windows endpoints must have Administrative Share and Network Share enabled.
Target Linux and Mac endpoints must have SSH enabled and firewall disabled.
You need to select one installation package for the current deployment. Click the Use package list and select the installation package that you want. You can find here all the installation packages previously created for your company.
If needed, you can modify some of the selected installation package's settings by clicking the button Customize next to the Use package field.
The installation package's settings will appear below and you can make the changes that you need. Find out more about editing installation packages here.
Warning
Please note that the Firewall module is available only for supported Windows workstations.
If you want to save the modifications as a new package, select the Save as package option placed at the bottom of the package settings list, and enter a name for the new installation package.
Click Save.
A confirmation message will appear.
Isolate endpoint
Isolate an endpoint in order to contain the spreading of potentially malicious activities, such as Lateral movement, to other endpoints in your network. When an endpoint is isolated, it can only communicate with GravityZone.
To isolate an endpoint:
Go to the Network page.
Select the container that you want from the left side pane. All endpoints from the selected container are displayed in the right side grid.
Select the checkbox of the endpoint you want to isolate.
Click the
 Tasks button at the upper side of the table and choose Isolate endpoint.
Tasks button at the upper side of the table and choose Isolate endpoint.Confirm your choice.
You can view and manage the task on the Network > Tasks page. For more information, refer to Viewing and managing tasks.
Isolated endpoints will also display a warning message in the General tab of the endpoint's Information window.

Note
For the Isolate endpoint option to be available, Customer companies require at least one of the products below:
GravityZone Business Security Premium
GravityZone Business Security Enterprise
GravityZone Security for Workstations
GravityZone Security for Servers
GravityZone EDR Cloud
GravityZone Security for Endpoints Physical Workstations
GravityZone Security for Endpoints Physical Servers
GravityZone Security for Endpoints Virtualized Environments VDI
GravityZone Security for Endpoints Virtualized Environments VS
GravityZone Security for Virtual Env per CPU
Security for AWS
If Customer companies have a Monthly subscription plan, they need to have Advanced Threat Security enabled.
Remove from isolation
To remove an endpoint from isolation and bring it back on the network:
Go to the Network page.
Select the container that you want from the left side pane. All endpoints from the selected container are displayed in the right side grid.
Select the checkbox of the endpoint you want to remove from isolation.
Click the
 Tasks button at the upper side of the table and choose Remove from isolation.
Tasks button at the upper side of the table and choose Remove from isolation.Confirm your choice.
Note
For the Isolate option to be available, Customer companies require at least one of the products below:
GravityZone Business Security Premium
GravityZone Business Security Enterprise
GravityZone Security for Workstations
GravityZone Security for Servers
GravityZone EDR Cloud
GravityZone Security for Endpoints Physical Workstations (version released in April 2022)
GravityZone Security for Endpoints Physical Servers (version released in April 2022)
GravityZone Security for Endpoints Virtualized Environments VDI (version released in April 2022)
GravityZone Security for Endpoints Virtualized Environments VS (version released in April 2022)
GravityZone Security for Virtual Env per CPU (version released in April 2022)
Security for AWS
If Customer companies have a Monthly subscription plan, they need to have Advanced Threat Security enabled.
Uninstall agent
To remotely uninstall the Bitdefender protection:
Go to the Network page.
Choose Virtual Machines from the views selector.
Select the container that you want from the left-side pane. All entities from the selected container are displayed in the right-side pane table.
Select the check boxes of virtual machines from which you want uninstall the Bitdefender security agent.
Click the
 Tasks button at the upper side of the table and choose Uninstall agent.
Tasks button at the upper side of the table and choose Uninstall agent.A configuration window is displayed, allowing you to opt for keeping the quarantined items on the client machine.
Click Save to create the task. A confirmation message will appear.
You can view and manage the task on the Network > Tasks page. For more information, refer to Viewing and managing tasks.
Note
If you want to reinstall protection, be sure to restart the computer first.
Update agent
Check the status of managed virtual machines periodically. If you notice a virtual machine with security issues, click its name to display the Information page. For more information, refer to Security Status.
Outdated clients or outdated security content represent security issues. In these cases, you should run an update on the corresponding virtual machines. This task can be done locally from the virtual machine, or remotely from Control Center.
To remotely update the client and the security content on managed virtual machines:
Go to the Network page.
Choose Virtual Machines from the views selector.
Select the container that you want from the left-side pane. All entities from the selected container are displayed in the right-side pane table.
Select the check boxes of virtual machines where you want to run a client update.
Click the
 Tasks button at the upper side of the table and choose Update agent. A configuration window will appear.
Tasks button at the upper side of the table and choose Update agent. A configuration window will appear.You can choose to update only the product, only the security content or both.
Click Update to run the task. A confirmation message will appear.
You can view and manage the task on the Network > Tasks page. For more information, refer to Viewing and managing tasks.
Upgrade agent
This task is available only when Endpoint Security agent is installed and detected in the network. Bitdefender recommends upgrading from Endpoint Security to Bitdefender Endpoint Security Tools Bitdefender Endpoint Security Tools, for a last-generation endpoint protection.
To easily find the security agents that are not upgraded, you can generate an upgrade status report. For details about how to create reports, refer to Creating reports.
Reconfigure agent
The security agent's protection modules, roles and scanning modes are initially configured within the installation package. After you have installed the security agent in your network, you can anytime change the initial settings by sending a Reconfigure agent remote task to the managed endpoints you are interested in.
Warning
Please note that Reconfigure agent task overwrites all installation settings and none of the initial settings is kept. While using this task, make sure to reconfigure all the installation settings for the target endpoints.
To change the installation settings for one or several virtual machines:
Go to the Network page.
Choose Virtual Machines from the views selector.
Select the container that you want from the left-side pane. All entities from the selected container are displayed in the right-side pane table.
Select the check boxes of virtual machines for which you want to change the installation settings.
Click the
 Tasks button at the upper side of the table and choose Reconfigure agent.
Tasks button at the upper side of the table and choose Reconfigure agent.Under the General section, configure the time when the task will run:
Now, to launch the task immediately.
Scheduled, to set up the task recurrence interval. In this case, select the time interval that you want (hourly, daily or weekly) and configure it according to your needs.
Note
For example, when other important processes are also required to run on the target machine, you can schedule the task to run every two hours. The task will start on each target machine every two hours until it is successfully done.
Configure the modules, roles and scan modes for the target endpoint as you want.
Warning
Only the supported modules for each operating system will be installed.
Please note that the Firewall module is available only for supported Windows workstations.
Bitdefender Tools (legacy agent) supports only Central Scan.
Click Save. A confirmation message will appear.
You can view and manage the task on the Network > Tasks page. For more information, refer to Viewing and managing tasks.
Restart endpoint
You can choose to remotely restart managed virtual machines.
Note
Check the Network > Tasks page before restarting certain virtual machines. Previously created tasks may still be processing on target machines.
This task is available only for distributed environments.
Go to the Network page.
Choose Virtual Machines from the views selector.
Select the container that you want from the left-side pane. All entities from the selected container are displayed in the right-side pane table.
Select the check boxes of virtual machines you want to restart.
Click the
 Tasks button at the upper side of the table and choose Restart endpoint.
Tasks button at the upper side of the table and choose Restart endpoint.Choose the restart schedule option:
Select Restart now to restart virtual machines immediately.
Select Restart on and use the fields below to schedule the restart at the desired date and time.
Click Save. A confirmation message will appear.
You can view and manage the task on the Network > Tasks page. For more information, refer to Viewing and managing tasks Viewing and Managing Tasks.
Run network discovery
Network discovery is done automatically only by security agents with Relay role. If you do not have a Relay agent installed in your network, you have to manually send a network discovery task from a protected endpoint.
To run a network discovery task in your network:
Go to the Network page.
Choose Virtual Machines from the views selector.
Select the container that you want from the left-side pane. All entities from the selected container are displayed in the right-side pane table.
Select the check box of the machine you want to perform network discovery with.
Click the
 Tasks button at the upper side of the table and choose Run network discovery.
Tasks button at the upper side of the table and choose Run network discovery.A confirmation message will appear. Click Yes.
You can view and manage the task on the Network > Tasks page. For more information, refer to Viewing and Managing Tasks.
Important
If using a Linux Relay to discover other Linux or Mac endpoints, you must either install Samba on target endpoints, or join them in Active Directory and use DHCP. This way, NetBIOS will be automatically configured on them.
Run applications discovery
To discover applications in your network:
Go to the Network page.
Choose Virtual Machines from the views selector.
Select the container that you want from the left-side pane. All virtual machines from the selected container are displayed in the right-side pane table.
Select the virtual machines on which you want to perform applications discovery.
Click the
 Tasks button at the upper side of the table and choose Run applications discovery.
Tasks button at the upper side of the table and choose Run applications discovery.Note
Bitdefender Endpoint Security Tools with Application Control must be installed and activated on the selected virtual machines. Otherwise, the task will be grayed out. When a selected group contains both valid and invalid targets, the task will be sent out only to valid endpoints.
Click Yes in the confirmation window to proceed.
The discovered applications and processes are displayed on the Network > Application inventory page. For more information, refer to Application inventory.
Note
The Run applications discovery task may take a while, depending on the number of applications installed. You can view and manage the task on the Network > Tasks page. For more information, refer to Viewing and managing tasks.
Install Security Server
To install a Security Server in your virtual environment:
Go to the Network page.
Choose Virtual Machines from the views selector.
Browse the Nutanix, VMware or Citrix inventory and select the check boxes corresponding to the desired hosts or containers (Nutanix Prism, vCenter Server, XenServer or datacenter). For a fast selection, you can directly select the root container (Nutanix Inventory, VMware Inventory or Citrix Inventory). You will be able to select hosts individually from the installation wizard.
Note
You cannot select hosts from different folders.
Click the
 Tasks button at the upper side of the table and choose Install Security Server from the menu.
Tasks button at the upper side of the table and choose Install Security Server from the menu.The Security Server Installation window is displayed.
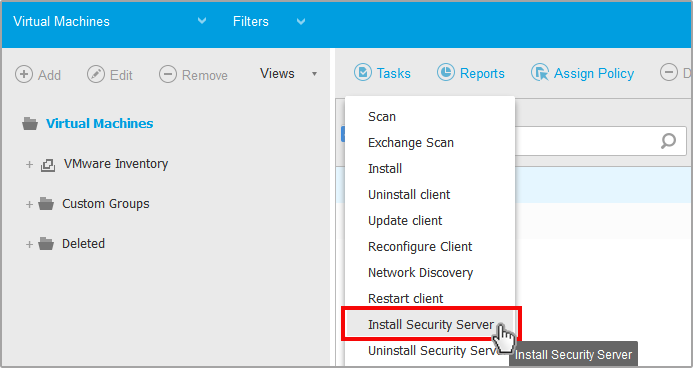
All the hosts detected in the selected container will appear in the list. Select the hosts on which you want to install the Security Server instances.
Choose the configuration settings you want to use.
Important
Using common settings while deploying multiple Security Server instances simultaneously requires the hosts to share the same storage, have their IP addresses assigned by a DHCP server and be part of the same network.
Click Next.
Enter a suggestive name for the Security Server.
For VMware environments, select the container in which you want to include the Security Server from the Deploy Container menu.
Select the destination storage.
Choose the disk provisioning type. It is recommended to deploy the appliance using thick disk provisioning.
Important
If you use thin disk provisioning and the disk space in the datastore runs out, the Security Server will freeze and, consequently, the host will remain unprotected.
Configure the memory and CPU resource allocation based on the VM consolidation ratio on the host. Choose Low, Medium or High to load the recommended resource allocation settings or Manual to configure resource allocation manually.
You have to set an administrative password for the Security Server console. Setting an administrative password overrides the default root password ("sve").
The administrative password must contain at least 8 characters, one digit, at least one upper case character, at least one lower case character, one special character and must be changed every 3 months.
Set the timezone of the appliance.
Select the network configuration type for the Bitdefender network. The IP address of the Security Server must not change in time, as it is used by Linux agents for communication.
If you choose DHCP, make sure to configure the DHCP server to reserve an IP address for the appliance.
If you choose static, you must enter the IP address, subnet mask, gateway and DNS information.
Click Save to create the task.
A confirmation message will appear.
Important
The Security Server packages are not included by default in the GravityZone appliance. Depending on the settings made by the root administrator, the Security Server package necessary for your environment will either be downloaded when a Security Server install task is launched or the administrator will be notified about the missing image and the installation will not proceed. If the package is missing, the root administrator will have to manually download it before the installation is possible.
Installing Security Server on Nutanix through remote task may fail when the Prism Element cluster is registered to Prism Central or because of another reason. In these situations, it is recommended to perform a manual deployment of Security Server.
You can view and manage the task on the Network > Tasks page. For more information, refer to Viewing and managing tasks.
Uninstall Security Server
To uninstall a Security Server:
Go to the Network page.
Choose Virtual Machines from the views selector.
Select the datacenter or folder containing the host on which the Security Server is installed.
Select the check box corresponding to the host on which the Security Server is installed.
Click the
 Tasks button at the upper side of the table and choose Uninstall Security Server.
Tasks button at the upper side of the table and choose Uninstall Security Server.You can view and manage the task on the Network > Tasks page. For more information, refer to Viewing and managing tasks.
Update Security Server
To update a Security Server:
Go to the Network page.
Choose Virtual Machines from the views selector.
Select the host on which the Security Server is installed.
To easily locate the Security Server, you can use the network.vms.search.filter Filters menu as follows:
Go to Security tab and select Security Servers only.
Go to Depth tab and select All items recursively.
Note
If you are using a virtualization management tool which is not currently integrated with Control Center, the Security Server will be placed under Custom Groups.
For more information regarding supported virtualization platforms, refer to Virtualization platforms,
Click the
 Tasks button at the upper side of the table and choose Update Security Server.
Tasks button at the upper side of the table and choose Update Security Server.Choose the type of update to perform:
Security features, for installing the Bitdefender new features, improvements and fixes, and security fixes
Operating system, for upgrading the operating system of the Security Server appliance
Note
Check the release notes to find out what type of update you are going to deploy.
Additionally, for the operating system update, select the time and date when the update should run. You can run it immediately or schedule it at a convenient time, such as a maintenance window.
Click OK to create the task.
You can view and manage the task on the Network > Tasks page. For more information, refer to Viewing and managing tasks.
Important
It is recommended to use this method to update the Security Server for NSX, otherwise you will lose the quarantine saved on the appliance.
Running tasks on mobile devices
From the Network page, you can remotely run a number of administrative tasks on mobile devices.
This is what you can do:
To run remote tasks on mobile devices, certain prerequisites must be met.
For more information, refer to the Installation chapter.
You can choose to create tasks individually for each mobile device, for each user or for groups of users.
For example, you can remotely scan for malware the mobile devices of a group of users.
You can also run a locate task for a specific mobile device.
The network inventory can contain active, idle or unmanaged mobile devices.
Once created, tasks will start running immediately on active mobile devices.
For idle devices, the tasks will start as soon as they get back online.
Tasks will not be created for unmanaged mobile devices.
A notification stating that the task could not be created will be displayed in this case.
You can view and manage tasks in the Network > Tasks page.
For more information, refer to Viewing and Managing Tasks.
Lock
The Lock task immediately locks the screen of target mobile devices.
The Lock task behavior is operating system dependent:
Lock task for Android devices (7.0 or above) will enforce the password set in your GravityZone console only if there is no lock protection configured on the device.
Otherwise, the existing screen lock options such as Pattern, PIN, Password, Fingerprint or Smart Lock will be used to protect the device.
Note
The lock screen password generated by Control Center is displayed in the Mobile Device Details window.
Unlock task is no longer available for Android devices (7.0 or above).
On iOS, if the device has a lock screen password, it is asked in order to unlock.
To remotely lock mobile devices:
Go to the Network page.
Choose Mobile Devices from the views selector.
Select the group that you want from the left-side pane.
Click the Filters menu at the upper side of the network panes area and select Users from the View category.
Click Save.
All users in the selected group are displayed in the table.
Select the check boxes corresponding to users you are interested in.
You can select one or several users at the same time.
Click the
 Tasks button at the upper side of the table and choose Lock.
Tasks button at the upper side of the table and choose Lock.Click Yes to confirm your action.
A message will inform you whether the task was created or not.
You can view and manage the task in the Network > Tasks page.
For more information, refer to Viewing and Managing Tasks.
Wipe
The Wipe task restores the target mobile devices to factory settings.
Run this task to remotely erase all sensitive information and applications stored on target mobile devices.
Warning
Use the Wipe task carefully.
Check the ownership of target devices (if you want to avoid wiping personally-owned mobile devices) and make sure that you really want to wipe the selected devices.
Once sent, the Wipe task cannot be undone.
To remotely wipe a mobile device:
Go to the Network page.
Choose Mobile Devices from the views selector.
Select the group that you want from the left-side pane.
Click the Filters menu at the upper side of the network panes area and select Devices from the View category.
Click Save.
All devices in the selected group are displayed in the table.
Note
You can also select All items recursively under the Depth section to view all devices in the current group.
Select the check box corresponding to the device you want to wipe.
Click the
 Tasks button at the upper side of the table and choose Wipe.
Tasks button at the upper side of the table and choose Wipe.Click Yes to confirm your action.
A message will inform you whether the task was created or not.
You can view and manage the task in the Network > Tasks page.
For more information, refer to Viewing and Managing Tasks.
Scan
The Scan task allows you to check selected mobile devices for malware.
The device user is notified about any detected malware and prompted to remove it.
The scan is performed in the cloud, therefore the device must have Internet access.
Note
The remote scan does not work on iOS devices (platform limitation).
To remotely scan mobile devices:
Go to the Network page.
Choose Mobile Devices from the views selector.
Select the group that you want from the left-side pane.
Click the Filters menu at the upper side of the network panes area and select Devices from the View category.
Click Save.
All devices in the selected group are displayed in the table.
Note
You can also select All items recursively under the Depth section to view all devices in the current group.
To display only Android devices in the selected group, go to the OS column header in the right-side pane and choose Android from the corresponding list box.
Select the check boxes corresponding to devices you want to scan.
Click the
 Tasks button at the upper side of the table and choose Scan.
Tasks button at the upper side of the table and choose Scan.Click Yes to confirm your action.
A message will inform you whether the task was created or not.
You can view and manage the task in the Network > Tasks page.
A scan report is available when the task completes.
Click the corresponding
 icon in the Reports column to generate an instant report.
icon in the Reports column to generate an instant report.For more information, refer to Viewing and Managing Tasks.
Locate
The Locate task opens a map showing the location of selected devices.
You can locate one or several devices at the same time.
For the Locate task to work, the location services must be enabled on the mobile devices.
To locate mobile devices:
Go to the Network page.
Choose Mobile Devices from the views selector.
Select the group that you want from the left-side pane.
Click the Filters menu at the upper side of the network panes area and select Devices from the View category.
Click Save.
All devices in the selected group are displayed in the table.
Note
You can also select All items recursively under the Depth section to view recursively all devices in the current group.
Select the check box corresponding to the device you want to locate.
Click the
 Tasks button at the upper side of the table and choose Locate.
Tasks button at the upper side of the table and choose Locate.The Location window opens, displaying the following information:
A map showing the position of the selected mobile devices.
If a device is not synchronized, the map will display its last known location.
A table displaying the details of selected devices (name, user, last synchronization date and time).
To view the map location of a certain device listed in the table, just select its check box.
The map will instantly focus on the corresponding device's location.
The Autorefresh option automatically updates the selected mobile devices locations after each 10 seconds.
You can view and manage the task in the Network > Tasks page.
For more information, refer to Viewing and Managing Tasks.