Best practices
Creating custom MAC address pools in Hyper-V
This section describes how to create custom MAC address pools in Hyper-V.
Using Hyper-V Dynamic MAC Address Regeneration can change the MAC address of a virtual machine which can lead to duplicate machines in the Control Center.
To avoid this issue, a custom MAC address pool can be created by following these steps:
Open the Fabric workspace.
On the Fabric pane, select Networking and click on MAC Address Pools.
On the Home tab, click on Fabric Resources.
On the Home tab, Create group, click on Create MAC Pool.
In Name and Host Group, populate the fields and click Next.
In MAC Address Range, specify the beginning and ending MAC address.
On the Summary page, confirm the settings and click Finish. Close the dialog box, after the status has changed to Completed.
Understanding Network discovery
This section explains how GravityZoneControl Center displays all your company's computers in Network inventory.
GravityZone includes an automatic network discovery mechanism intended to detect workgroup computers.
Security for Endpoints relies on the Microsoft Computer Browser service to perform network discovery. The Computer Browser service is a networking technology used by Windows-based computers to maintain updated lists of domains, workgroups, and the computers within them and to supply these lists to client computers upon request. Computers detected in the network by the Computer Browser service can be viewed by running the net view command in a Command Prompt window.

To enable Network Discovery, you must have the Bitdefender security agent already installed on at least one computer in the network. This computer will be used to scan the network.
You can enable the automatic network discovery by selecting the Automatic Discovery of new endpoints check box in Relay > Communication section of the policy settings.
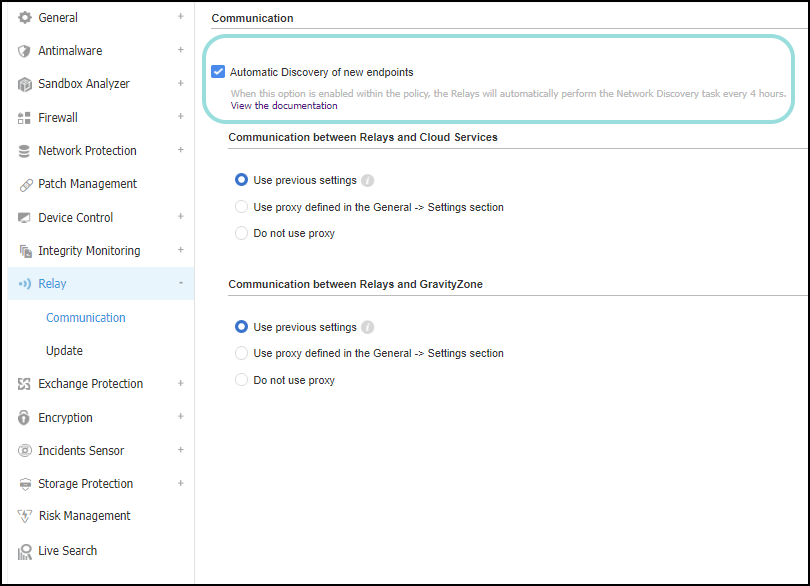
Activating this option determines the relays to perform the Network discovery task every 4 hours.
This option is disabled by default for new GravityZone users. For existing custom policies, the option remains enabled.
In order to successfully discover all the computers (servers and workstations) that will be managed from Control Center, the following are required:
Computers must be joined in a workgroup or domain and connected via an IPv4 local network. Computer Browser service does not work over IPv6 networks.
Several computers in each LAN group (workgroup or domain) must be running the Computer Browser service. Primary Domain Controllers must also run the service.
NetBIOS over TCP/IP (NetBT) must be enabled on computers. Local firewall must allow NetBT traffic.
File sharing must be enabled on computers. Local firewall must allow file sharing.
A Windows Internet Name Service (WINS) infrastructure must be set up and working properly.
For Windows 7 and later, Network discovery must be turned on (Control Panel > Network and Sharing Center > Change Advanced Sharing Settings).
To be able to turn on this feature, the following services must first be started:
DNS Client
Function Discovery Resource Publication
SSDP Discovery
UPnP Device Host
In environments with multiple domains, it is recommended to set up trust relationships between domains so that computers can access browse lists from other domains.
Computers from which Endpoint Security queries the Computer Browser service must be able to resolve NetBIOS names.
Note
The Network discovery mechanism works for all supported operating systems, including Windows Embedded versions, provided the requirements are met.
Identifying Linux endpoints joined in Active Directory
This section describes how you can view Linux endpoints joined in Active Directory in the proper domain tree and not in Custom Groups.
Bitdefender GravityZone integrates with multiple Microsoft Active Directory (AD) domains, provided you use this network management system in your network. Through AD integration, the existing AD inventory is imported into Control Center, thus simplifying security deployment, management, monitoring and reporting.
While GravityZone automatically recognizes Windows endpoints in Active Directory, for Linux endpoints you must perform a couple of operations.
Prerequisite
BEST, the Bitdefender security agent, must be installed on endpoints.
Identifying Linux endpoints in Active Directory
To properly identify Linux endpoints that are part of an Active Directory domain, follow these steps:
Download the ldbsearch tool. This tool is used to retrieve accurate domain information.
On each of your Linux endpoints in AD:
Update the repositories.
Install the ldbsearch tool.
Restart BEST services and acquire domain information.
For example, on Ubuntu run the following commands (via SSH TTY or in a BASH script):
# sudo apt-get update
# sudo apt-get install ldb-tools
# sudo bd restart
For other Linux distributions, please check the link exposed above.
As a result, BEST sends the information to Control Center and the endpoint will be dispatched as being part of an AD domain.
You can find the Linux endpoints detected in AD under the specific domain tree in the Network page of Control Center, using the Computers and Virtual Machines view.
Managing endpoints outside the company's network
The purpose of this section is to guide GravityZone (On-Premises) administrators to manage endpoints outside the company network.
Configure a port forwarding rule
In the default GravityZone setup, you can manage the endpoints only when they are directly connected to the corporate network.
To manage BEST over the Internet, you need to configure port forwarding on the corporate gateway for the appliance running the Communication Server role. Consequently translating the public IP address and port 8443 to GravityZone's Communication Server IP.
Install Bitdefender Endpoint Security Tools (BEST)
You can deploy Bitdefender Endpoint Security Tools on an endpoint:
Locally, by running an installation package.
Remotely, by running an installation task from the GravityZone Control Center.
For more information, refer to Install security agents - standard procedure.
Create and assign a custom policy
Endpoints are initially assigned with the default policy. You need to create and assign a specific policy for endpoints located outside the corporate network.
To create a custom policy for this scenario follow these steps:
Go to the Policies page.
Click the Add button at the upper side of the table to create a new policy.
Choose a suggestive name for the policy and enter it in the General > Details section of the policy.
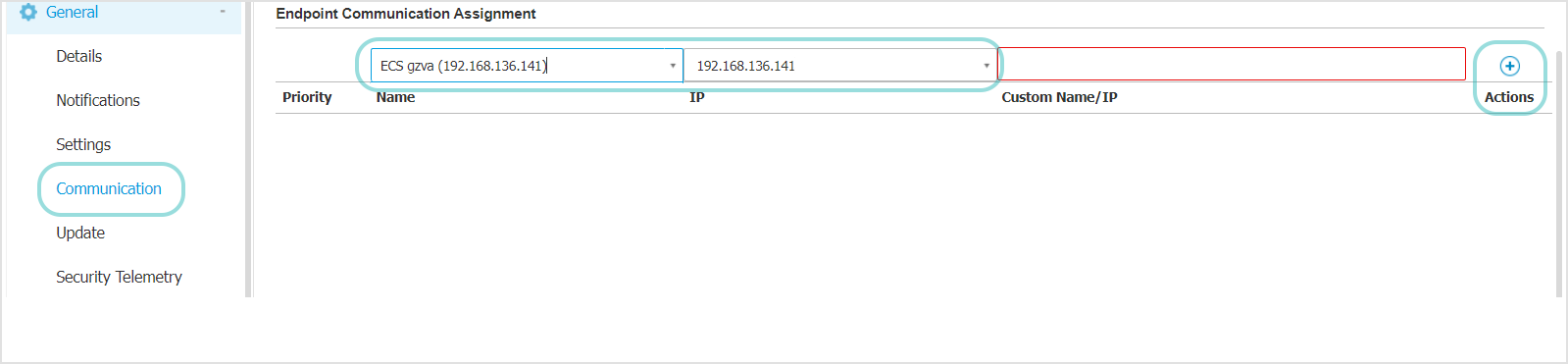
Go to General > Communication section.
In the Endpoint Communication Assignment table choose the Communication Server for which you have configured port forwarding, from the Name drop-down menu.
Replace the value displayed in the Custom Name/IP field with the public IP address of the Communication Server.
Click the Add button at the right side of the table to assign the Communication Server.
In the Update section, check that the check box Use upgrade.bitdefender.com as fallback location is selected.
Configure other policy settings according to your needs. For details, refer to the Configuring computer and virtual machine policies.
Save the policy.
Endpoints inside the company’s network receive updates from the GravityZone Update Server. In the Update policy section, the Use upgrade.bitdefender.com as fallback location check box is selected by default. If the update locations are unavailable, the fallback location will be used.
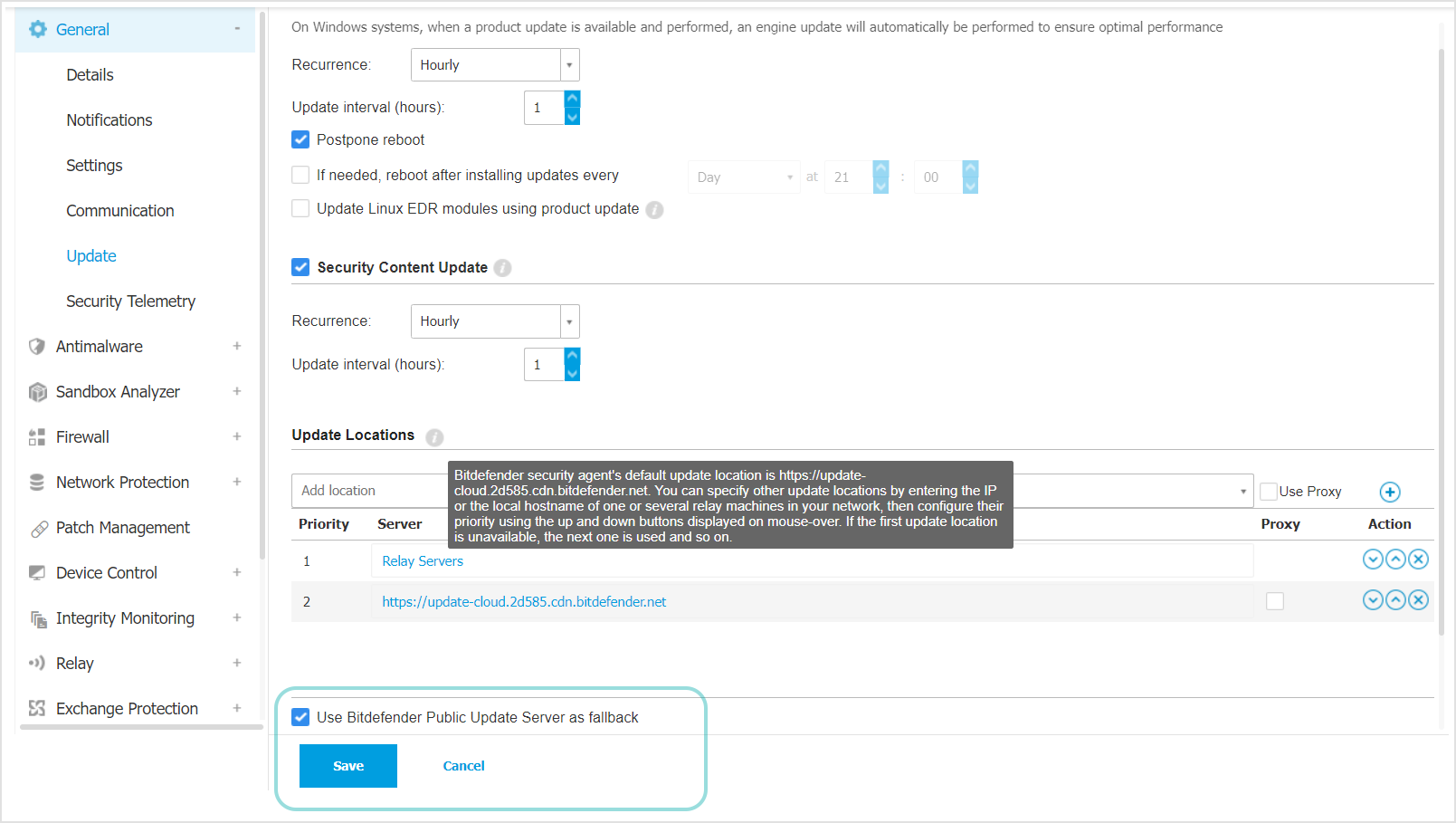
If the endpoint is located outside the network, the operation will fail and the endpoint will use the public IP address instead.
To assign the policy:
Go to the Network page.
Select Computers and Virtual Machines from the views selector.
Select the endpoints which go outside the company premises.
Click the Assign Policy button at the upper side of the table. Alternatively, you can right-click the selection and use the contextual menu to assign the policy.
Choose your policy from the drop-down menu.
Click Finish to save and apply changes.